Hypertension
- Persistently elevated Blood Pressure
- Uncontrolled hypertension is a risk factor for:
- MI
- Stroke
- CRF ( Chronic Renal Failure)
- Blindness
- “ Silent Killer “- Leading cause of death
2017 AHA/ACC : Categories of BP in Adults*
| BP Category |
SBP |
|
DBP |
| Normal |
<120 mm Hg |
and |
<80 mm Hg |
| Elevated |
120–129 mm Hg |
and |
<80 mm Hg |
| Hypertension |
| Stage 1 |
130–139 mm Hg |
or |
80–89 mm Hg |
| Stage 2 |
≥140 mm Hg |
or |
≥90 mm Hg |
*Individuals with SBP and DBP in 2 categories should be designated to the higher BP category.
BP Thresholds for and Goals of Pharmacological Therapy in Patients With Hypertension According to Clinical Conditions
| Clinical Condition(s) |
BP Threshold, mm Hg |
BP Goal, mm Hg |
| General |
| Clinical CVD or 10-year ASCVD risk ≥ 10% |
≥ 130/80 |
<130/80 |
| No clinical CVD and 10-year ASCVD risk <10% |
≥ 140/90 |
<130/80 |
| Older persons (≥65 years of age; noninstitutionalized, ambulatory, community-living adults) |
≥ 130 (SBP) |
<130 (SBP) |
| Specific comorbidities |
| Diabetes mellitus |
≥ 130/80 |
<130/80 |
| Chronic kidney disease |
≥ 130/80 |
<130/80 |
| Chronic kidney disease after renal transplantation |
≥ 130/80 |
<130/80 |
| Heart failure |
≥ 130/80 |
<130/80 |
| Stable ischemic heart disease |
≥ 130/80 |
<130/80 |
| Secondary stroke prevention |
≥ 140/90 |
<130/80 |
| Secondary stroke prevention (lacunar) |
≥ 130/80 |
<130/80 |
| Peripheral arterial disease |
≥ 130/80 |
<130/80 |
ASCVD indicates atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BP, blood pressure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Canadian Hypertension guidelines 2017
What’s new?
- Longer acting (thiazide-like- Chlorthalidone) diuretics are preferred vs. shorter acting (Hydrochlorothiazide)
- Single pill combinations should be used as a first line treatment (regardless of the extent of BP elevation)
Anti-hypertensive Drugs
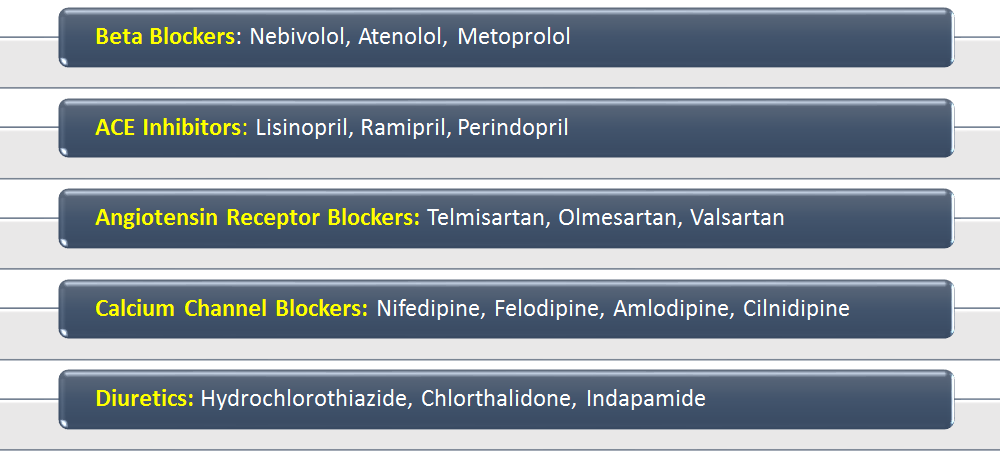
All agents are first-line and equally effective, some offer additional benefits in co-morbid conditions…
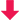
Telmisartan: Bifunctional ARB
Selectively blocks AT1 receptor + Activates PPAR Gamma receptor
Telmisartan: Unique ARB
- Only ARB which is approved for primary prevention of MI and stroke.
- Longest half life (>24 hrs) of all ARBs; better patient compliance with single daily dose.
- Better 24-hour BP control.
- Acts as a selective modulator of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), a central regulator of insulin and glucose metabolism- improves control of diabetes and lowers serum lipids ( LDL-C,TG)
- Telmisartan also appears to improve renal function
- No need to adjust dose in renal impairment
Amlodipine: Actions
- Long – acting calcium channel blocker
- Dilates peripheral arterioles and lowers peripheral vascular resistance
- Once daily dose, controls BP for 24 hours
- No adverse effect on glucose metabolism- safe in diabetics
- No adverse effect on serum lipid levels or sexual functions
- Very well tolerated
- Additive anti-hypertensive action, when combined with Diuretics/Beta blockers/ACEI/ARB
Chlorthalidone Vs Hydrochlorothiazide
- Long acting Thiazide-like Diuretic-Acts on kidneys- increases urine output and sodium excretion- lowers blood volume
- Longer half life-longer duration of action:
- 40-72 hr (vs. 6-15 hr for hydrochlorothiazide)
- Better 24 hr BP control
- More potent (~2x)
- 12.5 mg chlorthalidone is equivalent to 25 mg hydrochlrothiazide
- Blood glucose lowering effect-beneficial in diabetics
- Lowers LDL-C, TC- Preferred in patients with dyslipidemia
Aztel Trio: Indications
- 40-72 hr (vs. 6-15 hr for hydrochlorothiazide)
- Hypertension (SBP > 160/DBP > 100)
- Not controlled with Telmisartan dual therapy
- Hypertensies with High C Risk
(existing CAD, multiple C risk Factors or Diabetes or CKD)
- Diabetic hypertensies
- Hypertensie with chronic kidney disease
| AZTEL TRIO |
DOSAGE CHART |
| Starting dose |
One Tablet Daily |
| Dose titration after 4-6 weeks |
Two Tablets Daily |
| Recommended time of administration |
Preferably in Morning |
| Mild to moderate Renal dysfunction |
No need for dose adjustment |
| Liver impairment |
Use with caution |